tests of rotator cuff tear|shoulder rotator cuff physical exam : supplier Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but . web21 de jun. de 2023 · A Lotofácil 2843 aconteceu na quarta-feira dia 21 de junho de 2023 com prêmio estimado em R$ 1,7 Milhão. Confira aqui o resultado do concurso 2843 e os .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Free blackjack, for example, offers players a great opportunity to test out basic strategies without the possibility of losing any cash. Similarly, . Ver mais
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .Introduction. Shoulder Exam. In examining a patient with a painful shoulder we should start with a general inspection, looking for musculoskeletal abnormalities and any associated functional deficits. Then, we can carry on some .
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with provocative tests of the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, teres minor and subscapularis, but . Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X-ray, this test can visualize bone spurs or other potential causes for your pain — such as . Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are .
Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as .A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of shoulder pain and disability among adults. Each year, almost 2 million people in the United States visit their doctors because of rotator cuff tears. A torn rotator cuff may weaken your shoulder. Doctors use a variety of tests to diagnose rotator cuff problems. Imaging tests, such as an MRI, are especially important for figuring out the specific cause of your pain. Differential Diagnoses . . Small rotator cuff .
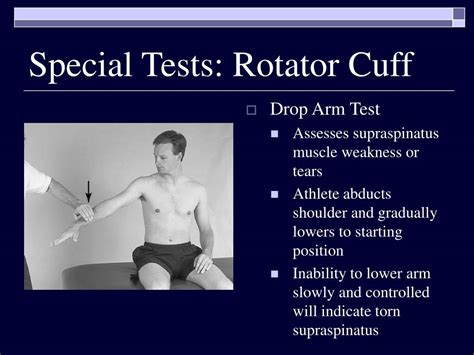
The rotator cuff can also be injured in a single incident during falls or accidents. Risk factors. The following factors may increase the risk of having a rotator cuff injury: Age. The risk of a rotator cuff injury increases with age. Rotator cuff tears are most common in people older than 60. Some occupations. A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm to . Rotator cuff injury runs the full spectrum from injury to tendinopathy to partial tears, and finally complete tears. Age plays a significant role. . When considering a rotator cuff tear, there are variations in the tests noted above. If the patient cannot hold the empty can test position, it is called a drop arm test. Next is the external .
Rotator cuff tear test There are many special tests doctors use to diagnose rotator cuff tear. Although they are not always reliable, you likely have a rotator cuff tear if you feel pain when .
special tests for rotator cuff tear
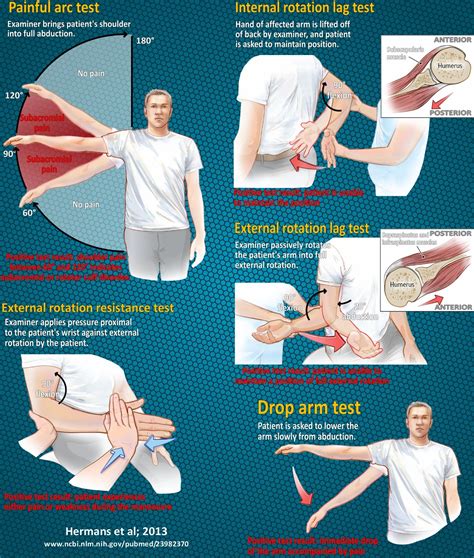
most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus. Infraspinatus Strength. technique. with the pateint's elbow in 90 degrees flexion, the arm at the side and internally rotated 45 degrees, external rotation strength can be checked against resistance by the examiner.To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [ edit | edit source ] Based on the Park et al [1] study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator . A rotator cuff tear is a tear in the group of four tendons and muscles surrounding the shoulder joint. Learn about symptoms and how it is treated surgically or conservatively. . Your healthcare provider may order one or several imaging tests to diagnose your condition accurately, including: X-rays; Ultrasound of the shoulder; MRI of the shoulder;The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus. This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies. The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
An injury to the rotator cuff, such as a tear, may happen suddenly when falling on an outstretched hand or develop over time because of repetitive activities. . This test uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to make detailed images of organs and structures within the body. A rotator cuff may tear partly or .Clinical Tests: The diagnosis of an RC tendinopathy can be done in a clinic with the use of Cluster Tests: The following Cluster Tests were retrieved from Roy et al. (2015): . For irreparable rotator cuff tears, alternative treatments include: Superior capsule reconstruction; Reverse total-shoulder arthroplasty;
This is the most common way to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and what type of tear it is. MRI results can provide information about the tear that can help the provider make certain decisions .
Rotator cuff injury test types. Which tests are performed may depend, in part, on whether your suspected rotator cuff injury is in the supraspinatus, subscapularis, or infraspinatus. and to determine whether the tendons that lie between the humerus and the acromion are being pinched . Rotator cuff tears are one of the most common injuries we see in orthopedic physical therapy. During the clinical examination of the shoulder, we want to perform special tests designed to detect a rotator cuff tear. Below are my 4 favorite special tests for rotator cuff tears that I perform during my clinical examination of the shoulder.This type of shoulder test, or rotator cuff injury test, is used to identify tears within the muscle group of the rotator cuff. Shoulder Shrug Test; This torn rotator cuff test checks if the patient imitates a shrug movement when trying to actively raise their arm. The patient is unable to raise the arm to a 90 degree elevation without raising . The Lateral Jobe Test is actually one of the most reliable tests for rotator cuff injury, and you may need an assistant again to help administer this test. This test also looks for weakness in the supraspinatus muscle. Begin by .
Occasionally, patients younger than 35 get partial tears of the rotator cuff. These tears may be associated with an injury. Partial rotator cuff tears are common in people who are overhead athletes (they play sports with an upper arm and shoulder arc over the head), such as pitchers in baseball. Partial rotator cuff tears in competitive . Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having the .A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of shoulder pain and disability among adults. Each year, almost 2 million people in the United States visit their doctors because of rotator cuff tears. . They will test your arm strength. Your doctor will test your range of motion by having you move your arm in different directions. Reproduced with .This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests .
Rotator cuff tear is a leading cause of shoulder pain resulting in varying degree of disability to perform activities of daily living. A methodical history taking and focussed clinical examination .Rotator cuff tendinopathy is the most common cause of shoulder pain. The supraspinatus tendon is most frequently involved and the subscapularis is second. Active abduction in an arc of 40 to 120° and internal rotation cause pain (see symptoms and signs of rotator cuff injury).Passive abduction causes less pain, but abduction against resistance can increase pain.
Rotator cuff tears, glenohumeral joint instabilities, and labral tears are associated with an increased incidence of subacromial impingement (1). The "cluster" of tests validated to rule in/rule out subacromial impingement only indicates the presence or absence of impingement (1). . The best combination of tests to detect a full-thickness RTC .The rotator cuff is a common cause of pain in the shoulder. Pain can happen because of: Tendinitis — inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons. Bursitis — inflammation of the bursa. Impingement — this happens because the space between the top of your shoulder (acromion) and the rotator cuff tendons becomes smaller when you raise your arm. A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11). Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner.
The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome.
shoulder rotator cuff physical exam
8 de out. de 2019 · Ouça. Imagens do circuito interno de um shopping no mostram momento em que Shanna Harrouche Garcia, filha do bicheiro Waldomiro Paes Garcia, o Maninho, foi baleada, na manhã desta terça .
tests of rotator cuff tear|shoulder rotator cuff physical exam